Coordinate Bond
A
covalent bond results from sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms,
where atom contributes one electron to the bond. It is also possible to have an
electron pair bond where both the electrons come from one of the two bonding atoms
and there is no contribution from the other atom. Such bonds are called
coordinate bonds or dative bonds, Coordinate
bond is a special type of covalent bond in which both the bonded electron come
from one of the two binding atoms. One common example is formation of ammonium
ion. Even though the ammonia molecule has electronic configuration it can react
with a hydrogen ion (H+) by donating a loan pair of electron from N
atom to H+ ion
forming the ammonium ion NH+4 .
Covalent
bonds are usually shown as a straight line joining the two atoms, and
coordinate bonds as arrows indicating which atom is donating the electron.
Similarly, ammonium donates its lone pair to boron trifluoride and by this
means the boron atom attains noble gas configuration.
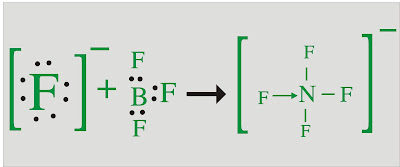
In
a similar way a molecule of BF3 can form a coordinate bond by
accepting a loan pair from a F- ion.
Double and Triple Bonds
Sometimes
more than two electrons are shared between a pair of atoms. If four electrons
are shared then there are two bonds this arrangement is called a double bond. If six electrons are
shared then there are three bonds and this is called a triple bond.




No comments:
Post a Comment